PathoPic – image database / PathoPic ID 11373 - Wiesner Naevus
de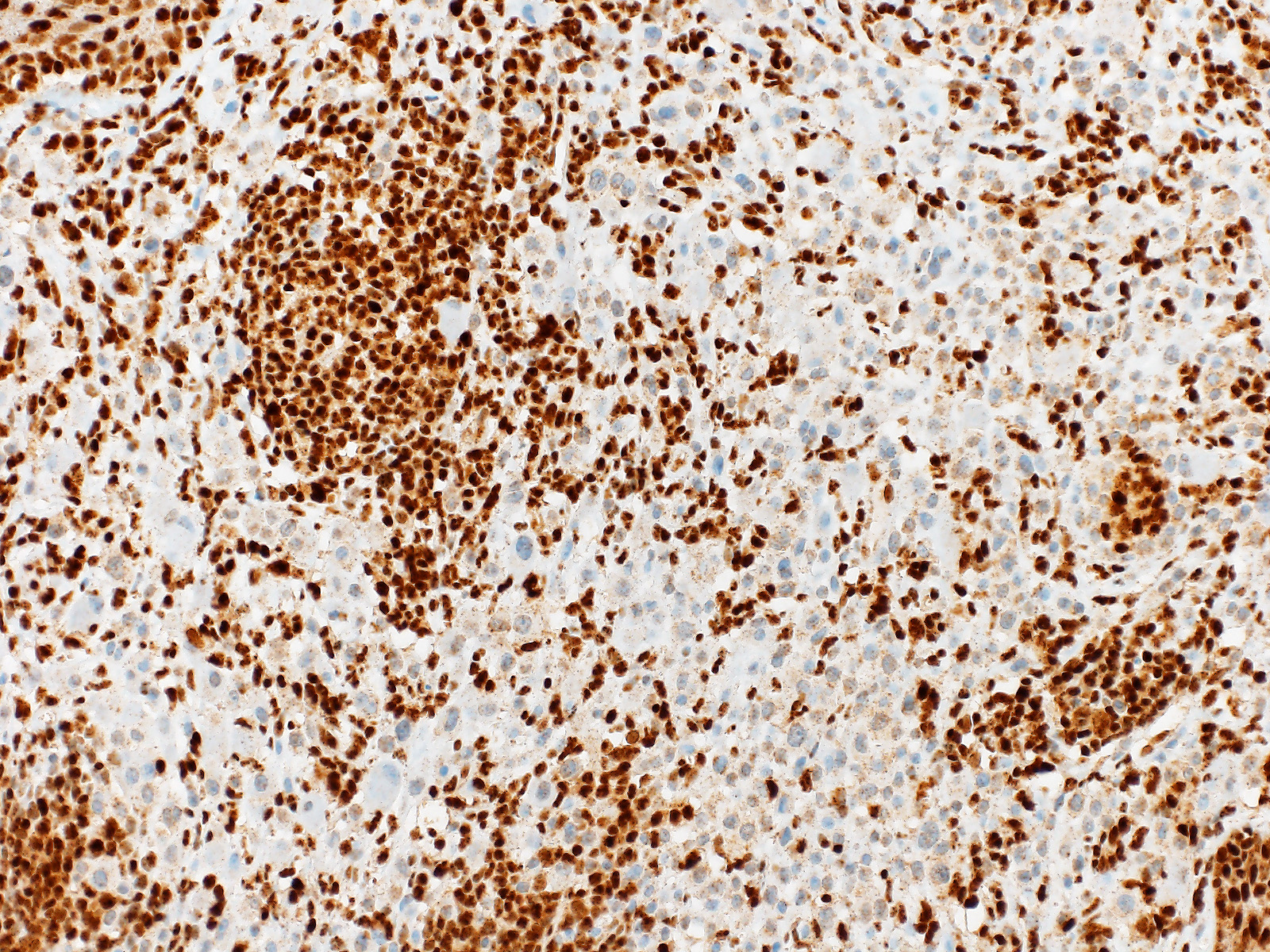
Diagnose
Wiesner Naevus
Diagnose Gruppe
benigner Tumor
Topographie
Haut, Rumpf
Topographie Gruppe
Haut
Beschreibung
Biphänotypischer, überwiegend intradermaler Naevus mit einer kleinzelligen gewöhnlichen Naevuskomponente und einer atypischen epitheloidzelligen Komponente. Die atypische Epitheloidzellkomponente zeigt einen Verlust der BAP1 Expression im Zellkern. In der konventionellen Naevuskomponente und in den tumorinfiltrierenden Lymphozyten ist die BAP1 Expression erhalten.
Zusatzbefund
Die grossen epitheloiden Zellproliferate zeigen einen Verlust der BAP1 Expression im Zellkern. Die Zellkerne des gewöhnlichen Naevusanteils sind positiv. Beide Komponenten sind immunhistochemisch positiv für die BRAF V600E Mutation.
Klinik
Papillomatöser Naevus am Rücken einer 21 jährigen Patientin.
Kommentar
In Wiesner's nevu, classic features of Spitz nevus, such as Kamino bodies, spindle-shaped melanocytes, epidermal hyperplasia and clefting around junctional melanocytic nests, are absent.
These tumors may be sporadic or appear multiple in patients with an autosomal dominant syndrome caused by germline mutations in BAP1. Both sporadic and Wiesner nevi in the familial syndrome show BRAF V600E mutation and loss of nuclear staining for BAP1.
If a BAP1 mutation is confirmed in a tumour, the patient's treating physician should be informed of the possibility of a BAP1 germline mutation, so they can consider whether genetic counselling and further testing of the patient and investigation of their family is appropriate.
Wiesner's nevi may present as a pure large epithelioid cell proliferation or as in this case as a combined lesion in association with a conventional nevus.
Pathology. 2013 Feb;45(2):116-26. Tumours associated with BAP1 mutations. Murali et al.
Am J Surg Pathol. 2013 Feb;37(2):193-9. Combined BRAF(V600E)-positive melanocytic lesions with large epithelioid cells lacking BAP1 expression and conventional nevomelanocytes. Busam et al.
Bilder Typ
Histologie
Immunhistochemie
BAP1
Vergrösserung
200
Alter
21
Geschlecht
unbekannt
Datum
Ersteintrag: 04.11.2015
Update: 04.02.2024